Summary
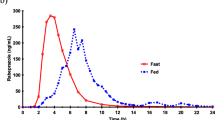
Rectal and oral absorption of valproic acid and its sodium salt by man were compared to explore the possibility of rectal administration of the drug. The plasma concentration of valproic acid was measured by gas chromatography after a single oral dose of sodium valproate 600 mg, and after single rectal doses of sodium valproate 600 mg and valproic acid 520 mg, in a cross-over study in 7 volunteers. The rectal dosage forms included fatty suppositories and aqueous solutions. Compared with oral administration, rectal absorption of sodium valproate from an aqueous micro-enema was fast and complete. The free acid was absorbed more rapidly from fatty suppositories than was the sodium salt. The absorption rate from the rectum increased with the dose of valproic acid. Both findings are consistent with a diffusion — absorption mechanism based on the pH-partition hypothesis. Differences in the chemical composition of the fatty suppository base were not reflected in differences in absorption rate and relative bioavailability. No essential difference in absorption rate was observed if volunteers remained lying or sitting during the experiment. Rectal dosing with valproic acid 520 mg dissolved in 4 ml suppositories, twice a day resulted in steady-state plasma concentrations of 50 to 100 µg · ml−1, within the therapeutic range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruni J, Wilder BJ, Willmore LJ, Perchalski RJ, Villarreal HJ (1978) Steady-state kinetics of valproic acid in epileptic patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 24: 324–332
DeBlaey CJ, Polderman J (1978) Rationales in the design of rectal and vaginal delivery forms of drugs. In: Ariens, EJ (ed) Drug design. Academic Press, London
Gugler R, Schell A, Eichelbaum M, Fröscher W, Schulz HV (1977) Disposition of valproic acid in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 12: 125–132
Klotz U, Antonin KH (1977) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of sodium valproate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 21: 736–743
Loiseau P, Brachet A, Henry P (1975) Concentration of dipropylacetate in plasma. Epilepsia 16: 609–615
Meunier H, Carraz G, Meunier V, Eymard M (1963) Proprietés pharmacodinamique de l'acide n-dipropylacetique. Therapie 18: 453–458
Meijer JWA, Hessing-Brand L (1973) Determination of lower fatty acids, particulary the antiepileptic dipropyl-acetic acid, in biological materials by means of micro diffusion and gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 43: 215–222
Moolenaar F, Schoonen AJM, Everts A, Huizinga T (1979) Absorption rate and bioavailability of paracetamol from fatty suppositories. Pharm Weekbl Sci Ed 1: 689–694
Pinder RM, Brodgen RN, Speight TM, Avery GS (1977) Sodium valproate: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs 13: 81–123
Queveauviller A, Jund J (1951) La médication par voie rectale evite-t-elle la barrière hepatique? Ann Pharm Fr 9: 593–601
Rutten-Kingma JJ (1977) Biofarmaceutisch onderzoek van suspensie-zetpillen. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Leiden, The Netherlands
Schobben F, van der Kleijn E (1974) Pharmacokinetics of distribution and elimination of sodium di-n-propylacetate in mouse and dog. Pharm Weekbl 109: 33–41
Schobben F, van der Kleijn E, Gabrieëls FJM (1975) Pharmacokinetics of di-n-propylacetate in epileptic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8: 97–105
Schoonen AJM, Moolenaar F, Haverschmidt C, Huizinga T (1976) The interphase transport of drugs from fatty suppository bases. Pharm. Weekbl 111: 585–590
Simon D, Penry JK (1975) Sodium di-n-propylacetate (DPA) in the treatment of epilepsy. A review. Epilepsie 16: 549–573
Sonnen AEH, Blom GF, Meijer JWA (1975) In: Schneider H, Janz D, Gardner-Thorpe C, Meinardi H, Sherwin AL (eds) Clinical pharmacology of anti-epileptic drugs. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Vajda FJE, Mihaly GW, Donnan GA, Bladin PF (1978) Rectal administration of sodium valproate in status epilepticus. Neurology 28: 897–899
Vree TB, Van der Kleijn E, Knop HJ (1976) Rapid determination of 4-hydroxybutyric acid (Gamma OH) and 2-propylpentanoate (Depakine) in human plasma by means of gas-liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr 121: 150–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Data have been presented in: F. Moolenaar, Ph. D. Thesis, Groningen, The Netherlands
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moolenaar, F., Greving, W.J. & Huizinga, T. Absorption rate and bioavailability of valproic acid and its sodium salt from rectal dosage forms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17, 309–315 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625806
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00625806