Summary
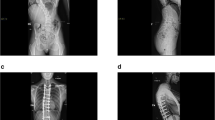
Fractures of the scapula are rare injuries. Usually the scapula requires a high-energy impact to sustain a fracture [l]. Various fractures have been noted as a result of convulsive seizures. We report bilateral scapular fractures caused by electric shock and discuss their pathomechanical origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hierholzer G, Hax Pm (1980) Scapulafraktur, Entstehung, Einteilung, Diagnose. Hefte Unfallheilkd 160:87–99
Mathews RE, Cocke TB, D'Ambrosia RD (1983) Scapula fractures secondary to seizures in patients with osteodystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 65:850–853
McGahan JP, Rab GT, Dublin A (1980) Fractures of the scapula. J Trauma 20:880–883
Mommsen U, Jungbluth KH (1980) Konservative Therapie und Behandlungsergebnisse der Scapulafrakturen. Hefte Unfallheilkd 160:100–104
Shaw JL (1971) Bilateral posterior fracture dislocation of the shoulder and other trauma caused by convulsive seizures. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 53:1437–1440
Tarquinio T, Weinstein ME, Virgilio R (1979) Bilateral scapula fractures from accidental electrical shock. J Trauma 19:132–133
Wilber MC, Evans EB (1977) Fractures of the scapula. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 59:358–362
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumas, J.L., Walker, N. Bilateral scapular fractures secondary to electrical shock. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 111, 287–288 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571527
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571527