Abstract
Nine premature infants with birth weight of 1150 to 2500 g and gestational age of 28 to 35 weeks were given dopamine in a dose of 2–4 μg/kg/min to treat cardiopulmonary distress.
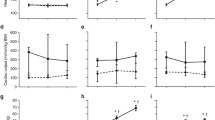
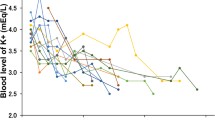
In addition to monitoring of blood gases, blood pressure, acid-base balance, urine flow and urinary sodium excretion, plasma renin activity (PRA) and plasma aldosterone concentration (PA) was also determined prior to and during dopamine therapy.
The dopamine-induced increase in urine flow and urinary sodium excretion was associated with a significant increase of PRA from 18.2±5.1 ng/ml/h to 33.0±5.6 ng/ml/h (P<0.025), while PA and blood pressure remained unaltered by dopamine administration.
It is suggested that the angiotensin II-stimulated aldosterone production is overridden by the inhibitory effect of dopamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RAAS:
-
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
- PRA:
-
plasma renin activity
- PA:
-
plasma aldosterone
References
Broughton-Pipkin F (1971) Cardiovascular responses in rabbits of different ages to hypertensin and adrenalin. Q J Exp Physiol 56:210–220
Broughton-Pipkin F, Oliver RC, Smales MRC (1977) A study of factors affecting blood pressure and angiotensin II in newborn infants. J Pediatr 91:113–119
Brown RD, Billman GE, Kem DC, Stone HL, Jiang N-S, Kao P, Hegstad RL (1982) The effect of metoclopramide and dopamine on plasma aldosterone concentration in normal man and Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta): A new model to study dopamine control of aldosterone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 55:828–832
Carey RM, Thorner MD, Ortt BM (1979) Effects of metoclopramide and bromocriptine on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in man. Dopaminergic control of aldosterone. J Clin Invest 63:727–735
Dillon MJ, Rajani KB, Shah V, Ryness MJ, Milner RDG (1978) Renin and aldosterone response in human newborns to acute change in blood volume. Arch Dis Child 53:461–467
Drummond WH, Gregory GA, Heymann MA, Phibbs RH (1981) The independent effects of hyperventilation, tolazoline and dopamine on infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 98:603–611
Godard C, Gaillard R, Vallotton MD (1976) The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in mother and fetus at term. Nephron 17:353–360
Haber E, Korner T, Page LB, Kliman B, Purnode A (1969) Application of radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurement of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 29:1349–1355
Hegyi T, Hiatt LM (1980) Tolazoline and dopamine in neonatal hypoxia and pulmonary vasospasm. Acta Paediatr Scand 69:101–103
Imbs J, Schmidt M, Schwartz J (1975) Effect of dopamine on renin secretion in the anaesthetized dog. Eur J Pharmacol 33:151–157
Kittermann JA, Phibbs RH, Tooley WH (1969) Aortic blood pressure in normal newborn infants during the first 12 hours of life. Pediatrics 44:959–966
Lagercrantz H, Bistoletti P (1977) Catecholamine release in the newborn infant at birth. Pediatr Res 11:889–893
McKenna TJ, Island DP, Nicholson WE, Liddle GW (1979) Dopamine inhibits angiotensin stimulated aldosterone biosynthesis in bovine adrenal cells. J Clin Invest 64:287–291
Seri I, Tulassay T, Kiszel J, Machay T, Csömör S (1984) Cardiovascular response to dopamine in hypotensive preterm infants with severe hyaline membrane disease. Eur J Pediatr 142:3–9
Siegel S (1981) Decreased vascular and increased adrenal and renal sensitivity to angiotensin II in the newborn lamb. Circ Res 48:34–38
Solc J, Knorr D (1974) Die Wirkung von Aldosteron und Spironolacton auf die Auscheidung von Natrium und Kalium in Harn bei Neugeborenen und Säuglingen. Z Kinderheilk 116:143–152
Solomon S, Iaina A, Eliahou H, Serban I (1977) Postnatal changes in plasma and renal renin of the rat. Biol Neonate 32:237–342
Sulyok E, Németh M, Tényi I, Csaba IF, Varga F, Györy E, Thurzó V (1979) Relationship between maturity, electrolyte balance and the function of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in newborn infants. Biol Neonate 35:60–65
Sulyok E, Németh M, Tényi I, Csaba IF, Györy E, Ertl T, Varga F (1979) Postnatal development of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in relation to electrolyte balance in premature infants. Pediatr Res 13:817–820
Sulyok E, Varga F, Németh M, Tényi I, Csaba IF, Ertl T, Györy E (1980) Furosemide-induced alterations in the electrolyte status, the function of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the urinary excretion of prostaglandins in newborn infants. Pediatr Res 14:765–768
Tulassay T, Seri I, Machay T, Kiszel J, Varga J, Csömör S (1983) Effects of dopamine on renal functions in premature neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Intern J Pediatr Nephrol 4:19–23
Vetter W, Vetter H, Siegenthaler W (1973) Radioimmunoassay for aldosterone without chromatography. 2. Determination of plasma aldosterone. Acta Endocrinol 74:558–567
Wilcox CS, Aminoff MJ, Kurtz AB, Slater JD (1974) Comparison of the renin response to dopamine and noradrenaline in normal subjects and patients with autonomic insufficiency. Clin Sci Mol Med 46:481–488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sulyok, E., Seri, I., Tulassay, T. et al. The effect of dopamine administration on the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in sick preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr 143, 191–193 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442135
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00442135