Summary
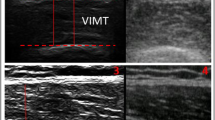
Real-time ultrasound scanning was used to measure the angles of fibre pennation of vastus lateralis (VL) and vastus intermedius (VI) of the human quadriceps (n = 12) in vivo. The maximum isometric force and cross-sectional area of the quadriceps were also measured. With the knee at right-angles the mean fibre angles for VL and VI respectively were 0.133 (0.021) rad [7.6° (1.2°)] and 0.143 (0.028) rad [8.2° (1.6°)] [mean (SD)], which is within the range of angles measured on cadavers. The mean angle decreased in going from the contracted [VL, 0.244 rad (14°); VI, 0.279 rad (16°)] to the stretched [VL, 0.105 rad (6°); VI, 0.122 rad (7°)] position. There was a significant positive correlation between fibre angle and muscle cross-sectional area but no relationship between fibre angle and force per cross-sectional area. No increase in fibre angle was detected after 3 months strength training. We conclude that ultrasound can be used to measure pennation angles of superficial muscle groups but we could not demonstrate a relationship between pennation and force-generating capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander R McN, Vernon A (1975) The dimensions of knee and ankle muscles and the forces they exert. J Hum Mov Stud 1:115–123
Bruce SA, Newton D, Woledge RC (1989) Effect of age on voluntary force and cross-sectional area of human adductor pollicis muscle. Q J Exp Physiol 74:359–362
Close RI (1972) Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev 52:129–197
Edwards RHT, Young A, Hosking GP, Jones DA (1977) Human skeletal muscle function: description of tests and normal values. Clin. Sci 52:283–290
Giannini F, Landoni L, Merella N, Minetti AE, Narici MV (1990) Estimation of specific tension of human knee extensor muscles from in vivo physiological CSA and strength measurements. J Physiol (Lond) 423:86P
Gollnick PD, Timson BF, Moore RL, Riedy M (1981) Muscular enlargement and number of fibres in skeletal muscles of rats. J Appl Physiol 50:936–943
Grindrod S, Tofts P, Edwards RHT (1983) Investigation of human skeletal muscle structure and composition by X-ray computerised tomography. Eur J Clin Invest 13:465–468
Henriksson-Larsen K, Wretling M-L, Lorentzon R, Oberg L (1992) Do muscle size and fibre angulation correlate in pennated human muscles? Eur J Appl Physiol 64:68–72
Jones DA, Rutherford OM (1990) Effect of ageing and osteoporosis on the force generating capacity of the quadriceps muscle in women. J Physiol (Loud) 423:84P
Jones DA, Rutherford OM, Parker DF (1989) Physiological changes in skeletal muscle as a result of strength training. Q J Exp Physiol 74:233–256
Maughan RJ, Watson JS, Weir J (1983) Strength and cross-sectional area of human skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 338:37–49
Narici MV, Roi GS, Landoni L (1988) Force of knee extensor and flexor muscles and cross-sectional area determined by nuclear-magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:39–44
Narici MV, Landoni L, Minetti AE (1992) Assessment of human knee extensor muscle stress from in vivo physiological crosssectional area and strength measurements. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:438–444
Pearson MB, Bassey EJ, Bendall MJ (1985) The effects of age on muscle strength and anthropometric indices within a group of elderly men and women. Age Ageing 14:230–234
Rutherford OM (1986) The determinants of human muscle strength and the effects of different high resistance training regimes. PhD Thesis, University of London
Rutherford OM, Jones DA, Newham DJ (1986) Clinical and experimental application of the twitch superimposition technique for the study of human muscle activation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1288–1291
Smidt GL (1973) Biomechanical analysis of knee flexion and extension. J Biomech 6:79–92
Wickiewicz TL, Roy RR, Powell PL, Edgerton VR (1983) Muscle architecture of the human lower limb. Clin Orthop 179:275–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutherford, O.M., Jones, D.A. Measurement of fibre pennation using ultrasound in the human quadriceps in vivo. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 433–437 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243510
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243510