Abstract
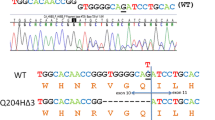
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by a deficiency of porphobilinogen deaminase (PBGD). Up to now 14 different mutations have been described. In an effort to investigate the molecular epidemiology of AIP we have undertaken a systematic study of different exons of the PBGD gene from a large number of unrelated patients. Here, exon 8 from 82 unrelated Dutch and French AIP patients was examined using single strand confirmation polymorphism analysis (SSCP) after polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. A single base mutation, C to T, at position 346 of the sequence coding for PBGD was observed in 15 Dutch families but in only 1 French family. A simple PCR assay is described to facilitate the diagnosis of this common mutation at the DNA level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaumont C, Porcher C, Picat C, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1989) The mouse porphobilinogen deaminase gene: structural organization, sequence, and transcriptional analysis. J Biol Chem 264:14829–14834
Bourgeois F, Gu XF, Deybach JC, Te Velde MP, De Rooij F, Normann Y, Grandchamp B (1992) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis for rapid detection of latent carriers of a subtype of acute intermittent porphyria with normal erythrocyte porphobilinogen deaminase activity. Clin Chem 38:93–95
Delfau MH, Picat C, Rooij FWM de, Hamer K, Bogard M, Wilson WHP, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1990) Two different point mutations G to A in exon 10 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene are responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. J Clin Invest 86:1511–1516
Delfau MH, Picat C, De Rooij F, Voortman G, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1991) Molecular heterogeneity of acute intermittent porphyria: four different new mutations result in a CRIM(-) subtype of the disease. Am J Hum Genet 49:421–428
De Rooij FWM, Hamer CM, Wilson JPH (1987) Heterogeneity in acute intermittent porphyria: biochemical evidence for family related variation in the mutant enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase. In: Topi GC, D'Alesandro-Gandolfo L (eds) Proceeding tof the international meeting on porphyrins and porphyrias. (Bolletino dell' Instituto Dermatologica S. Gallicano, vol XIII) Rome, pp 175–180
Desnick RJ, Ostasiewicz LT, Tishler PA, Mustajoki P (1985) Acute intermittent porphyria: characterization of a novel mutation in the structural gene for porphobilinogen deaminase. J Clin Invest 86:865–874
Eiken HG, Odland E, Boman H, Skjelkvale L, Engebretsen LF, Apold J (1991) Application of natural and amplification created restriction sites for the diagnosis of PKU mutation. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1427–1430
Grandchamp B, Picat C, Mignotte V, Wilson JHP, Te Velde K, Sandkuyl L, Romeo PH, Goossens M, Nordmann Y (1989a) Tissue specific splicing mutation in acute intermittent porphyria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:661–664
Grandchamp B, Picat C, Kaupinen R, Mignotte V, Peltonen L, Mustajoki P, Romeo PH, Goossens M, Nordmann Y (1989b) Molecular analysis of acute intermittent porphyria in a Finnish family with normal erythrocyte porphobilinogen deaminase. Eur J Clin Invest 19:415–418
Grandchamp B, Picat C, de Rooij F, Beaumont C, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y (1989c) A point mutation G/A in exon 12 of the PBG deaminase gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6637–6649
Gu XF, De Rooij FWM, Voortman G, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1991) Detection of acute intermittent porphyria mutation using DGGE. Am J Hum Genet 49 [Suppl]:A189
Higuchi R (1989) Principles and applications for DNA amplification. In: Erlich HA (ed) PCR technology. Stockton Press, London, pp 31–38
Hutman T, Stahl S, Hornes E, Mathias U (1989) Direct sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res 17:4937–4946
Jacobson DR, Moskovits T (1991) Rapid, nonradioactive screening for activating ras oncogene mutations using PCR-primer introduced restriction analysis (PCR-PIRA). PCR Methods Appl 1:146–148
Kappas A, Sassa S, Galbraith RA, Nordmann Y (1989) the porphyrias. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1305–1365
Lee JS, Anvret M (1991) Identification of the most common mutation within the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in Swedish patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10912–10915
Lee JS, Grandchamp B, Anvret M (1990) A point mutation of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene in a Swedish family with acute intermittent porpyria. Am J Hum Genet 47 [Suppl]:A162
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 466–467
Orita M, Suzeki Y, Sekiya T, Hayashi K (1989) A rapid and sensitive detection of point mutation and genetic polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5:874–879
Saiki KR, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Scobie GA, Llewellyn DH, Urquhart AJ, Smyth SJ, Kalsheker NA, Harrison PR (1990) Acute intermittent porphyria caused by a C to T mutation that produces a stop codon in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Hum Genet 85:631–634
Sharif AL, Smith AG, Abell C (1989) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for a chlorophyll synthesis enzyme in Euglena gracilis. Eur J Biochem 184:353–359
Stubnicer AC, Picat C, Grandchamp B (1988) Rat porphobilinogen deaminase cDNA: nucleotide sequence of the erythropoietic form. Nucleic Acids Res 16:3102
Thomas SD, Jordan P (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the hemC locus encoding porphobilinogen deaminase of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6215–6226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, XF., de Rooij, F., Lee, J.S. et al. High prevalence of a point mutation in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in Dutch patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Hum Genet 91, 128–130 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222712
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222712