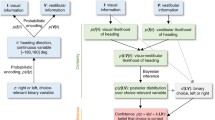
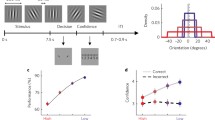
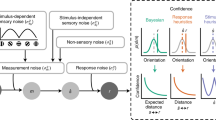
Abstract
Confidence judgments, the self-assessment of the quality of a subject’s knowledge, are considered a central example of metacognition. Prima facie, introspection, and self-report appear the only way to access the subjective sense of confidence or uncertainty. Could confidence be also studied in nonhuman animals so one could probe its neural substrates? Indeed, behavioral paradigms that incentivize animals to evaluate and act upon their own confidence can yield implicit reports of confidence. Here, we suggest that a computational approach can clarify the issues involved in interpreting these tasks and provide a much-needed springboard for advancing the scientific understanding of confidence. We first review relevant theories of probabilistic inference and decision making. We then critically discuss behavioral tasks employed to measure confidence in animals and show how quantitative models can help to constrain the computational strategies underlying confidence-reporting behaviors. In our view, post-decision wagering tasks with continuous measures of confidence appear to offer the best available metrics of confidence. Since behavioral reports alone provide a limited window into mechanism, we argue that progress calls for measuring the neural representations and identifying the computations underlying confidence reports. We present a case study using such a computational approach to study the neural correlates of decision confidence in rats. This work shows that confidence assessments may be considered higher order, but can be generated using elementary neural computations that are available to a wide range of species. Finally, we discuss the relationship of confidence judgments to the broader behavioral uses of confidence and uncertainty.
This chapter is adapted from: Kepecs A, Mainen ZF (2012) A computational framework for the study of confidence in humans and animals. Phil Trans R Soc B 367:1322–1337
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flavell JH (1979) Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: a new area of cognitive-developmental inquiry. Am Psychol 34:906–911
Metcalfe J, Shimamura AP (1994) Metacognition: knowing about knowing. MIT Press, Cambridge
Bjork RA (1994) Memory and metamemory considerations in the training of human beings. In: Metacognition: knowing about knowing. MIT Press, Cambridge
Metcalfe J (2008) Evolution of metacognition. In: Handbook of metamemory and memory, pp 185–205, 29–46
Smith JD, Shields WE, Washburn DA (2003) The comparative psychology of uncertainty monitoring and metacognition. Behav Brain Sci 26:317–339 (discussion 340–373)
Cox DR (2006) Principles of statistical inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Zemel RS, Dayan P, Pouget A (1998) Probabilistic interpretation of population codes. Neural Comput 10:403–430
Rao RPN, Olshausen BA, Lewicki MS (2002) Probabilistic models of the brain: perception and neural function. The MIT Press, Cambridge
Knill DC, Pouget A (2004) The Bayesian brain: the role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation. Trends Neurosci 27:712–719
Ma WJ, Beck JM, Latham PE, Pouget A (2006) Bayesian inference with probabilistic population codes. Nat Neurosci 9:1432–1438
Rao RP (2004) Bayesian computation in recurrent neural circuits. Neural Comput 16:1–38
Higham PA (2007) No special K! A signal detection framework for the strategic regulation of memory accuracy. J Exp Psychol Gen 136:1–22
Charles L, Van Opstal F, Marti S, Dehaene S (2013) Distinct brain mechanisms for conscious versus subliminal error detection. Neuroimage 73:80–94
McCurdy LY, Maniscalco B, Metcalfe J, Liu KY, de Lange FP, Lau H (2013) Anatomical coupling between distinct metacognitive systems for memory and visual perception. J Neurosci 33:1897–1906
Johnson DM (1939) Confidence and speed in the two-category judgment. Columbia University, Ney York
Festinger L (1943) Studies in decision: I. Decision-time, relative frequency of judgment and subjective confidence as related to physical stimulus difference. J Exp Psychol 32:291–306
Baranski JV, Petrusic WM (1994) The calibration and resolution of confidence in perceptual judgments. Percept Psychophys 55:412–428
Fleming SM, Weil RS, Nagy Z, Dolan RJ, Rees G (2010) Relating introspective accuracy to individual differences in brain structure. Science 329:1541–1543
Yokoyama O, Miura N, Watanabe J, Takemoto A, Uchida S, Sugiura M, Horie K, Sato S, Kawashima R, Nakamura K (2010) Right frontopolar cortex activity correlates with reliability of retrospective rating of confidence in short-term recognition memory performance. Neurosci Res 68:199–206
Fleming SM, Huijgen J, Dolan RJ (2012) Prefrontal contributions to metacognition in perceptual decision making. J Neurosci 32:6117–6125
Gigerenzer G, Hoffrage U, Kleinbolting H (1991) Probabilistic mental models: a Brunswikian theory of confidence. Psychol Rev 98:506–528
Klayman J, Soll JB, González-Vallejo C, Barlas S (1999) Overconfidence: it depends on how, what, and whom you ask. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 79:216–247
Finn B (2008) Framing effects on metacognitive monitoring and control. Mem Cognit 36:813–821
Angell F (1907) On judgments of “like” in discrimination experiments. Am J Psychol 253–260
Watson CS, Kellogg SC, Kawanishi DT, Lucas PA (1973) The uncertain response in detection-oriented psychophysics. J Exp Psychol 99:180–185
Woodworth RS (1938) Experimental psychology. Henry Holt and Company Inc, New York
Peirce CS, Jastrow J (1885) On small differences of sensation. Mem Natl Acad Sci 3:73–83
George SS (1917) Attitude in relation to the psychophysical judgment. Am J Psychol 28:1–37
Smith JD, Schull J, Strote J, McGee K, Egnor R, Erb L (1995) The uncertain response in the bottlenosed dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). J Exp Psychol Gen 124:391–408
Smith JD, Schull J (1989) A failure of uncertainty monitoring in the rat. (unpublished data)
Shields WE, Smith JD, Washburn DA (1997) Uncertain responses by humans and rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) in a psychophysical same-different task. J Exp Psychol Gen 126:147–164
Smith JD, Shields WE, Schull J, Washburn DA (1997) The uncertain response in humans and animals. Cognition 62:75–97
Shields WE, Smith JD, Guttmannova K, Washburn DA (2005) Confidence judgments by humans and rhesus monkeys. J Gen Psychol 132:165–186
Beran MJ, Smith JD, Redford JS, Washburn DA (2006) Rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) monitor uncertainty during numerosity judgments. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 32:111–119
Sole LM, Shettleworth SJ, Bennett PJ (2003) Uncertainty in pigeons. Psychon Bull Rev 10:738–745
Komura Y, Nikkuni A, Hirashima N, Uetake T, Miyamoto A (2013) Responses of pulvinar neurons reflect a subject’s confidence in visual categorization. Nat Neurosci 16:749–755
Smith JD, Beran MJ, Redford JS, Washburn DA (2006) Dissociating uncertainty responses and reinforcement signals in the comparative study of uncertainty monitoring. J Exp Psychol Gen 135:282–297
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning: an introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge
Hampton RR (2001) Rhesus monkeys know when they remember. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5359–5362
Kiani R, Shadlen MN (2009) Representation of confidence associated with a decision by neurons in the parietal cortex. Science 324:759–764
Inman A, Shettleworth SJ (1999) Detecting metameory in nonverbal subjects: a test with pigeon. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 25:389–395
Teller SA (1989) Metamemory in the pigeon: prediction of performance on a delayed matching to sample task. Reed College
Sutton JE, Shettleworth SJ (2008) Memory without awareness: pigeons do not show metamemory in delayed matching to sample. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 34:266
Foote AL, Crystal JD (2007) Metacognition in the rat. Curr Biol 17:551–555
Kepecs A (2013) The uncertainty of it all. Nat Neurosci 16:660–662
Persaud N, McLeod P, Cowey A (2007) Post-decision wagering objectively measures awareness. Nat Neurosci 10:257–261
Persaud N, McLeod P (2008) Wagering demonstrates subconscious processing in a binary exclusion task. Conscious Cogn 17:565–575
Sahraie A, Weiskrantz L, Barbur JL (1998) Awareness and confidence ratings in motion perception without geniculo-striate projection. Behav Brain Res 96:71–77
Rajaram S, Hamilton M, Bolton A (2002) Distinguishing states of awareness from confidence during retrieval: evidence from amnesia. Cognitive, Affect Behav Neurosci 2:227–235
Son LK, Kornell N (2005) Meta-confidence judgments in rhesus macaques: explicit versus implicit mechanisms. In: Terrace HS, Metcalfe J (eds) The missing link in cognition: origins of self-reflective consciousness. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 296–320
Kornell N, Son LK, Terrace HS (2007) Transfer of metacognitive skills and hint seeking in monkeys. Psychol Sci 18:64–71
Middlebrooks PG, Sommer MA (2010) Metacognition in monkeys during an oculomotor task. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 37:325–337
Middlebrooks PG, Sommer MA (2012) Neuronal correlates of metacognition in primate frontal cortex. Neuron 75:517–530
Clifford CW, Arabzadeh E, Harris JA (2008) Getting technical about awareness. Trends Cogn Sci 12:54–58
Fleming SM, Dolan RJ (2010) Effects of loss aversion on post-decision wagering: implications for measures of awareness. Conscious Cogn 19:352–363
Schurger A, Sher S (2008) Awareness, loss aversion, and post-decision wagering. Trends Cogn Sci 12:209–210 (author reply 210)
Kepecs A, Uchida N, Zariwala HA, Mainen ZF (2008) Neural correlates, computation and behavioural impact of decision confidence. Nature 455:227–231
Call J, Carpenter M (2001) Do apes and children know what they have seen? Animal Cognition 3:207–220
Hampton RR, Zivin A, Murray EA (2004) Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) discriminate between knowing and not knowing and collect information as needed before acting. Anim Cogn 7:239–246
Radecki CM, Jaccard J (1995) Perceptions of knowledge, actual knowledge, and information search behavior. J Exp Soc Psychol 31:107–138
Basile BM, Hampton RR, Suomi SJ, Murray EA (2009) An assessment of memory awareness in tufted capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella). Anim Cogn 12:169–180
Brauer J, Call J, Tomasello M (2007) Chimpanzees really know what others can see in a competitive situation. Anim Cogn 10:439–448
Suda-King C (2008) Do orangutans (Pongo pygmaeus) know when they do not remember? Anim Cogn 11:21–42
Brauer J, Call J, Tomasello M (2004) Visual perspective taking in dogs (Canis familiaris) in the presence of barriers. Appl Anim Behav Sci 88:299–317
Brauer J, Kaminski J, Riedel J, Call J, Tomasello M (2006) Making inferences about the location of hidden food: social dog, causal ape. J Comp Psychol 120:38–47
Bromberg-Martin ES, Hikosaka O (2009) Midbrain dopamine neurons signal preference for advance information about upcoming rewards. Neuron 63:119–126
Shettleworth SJ, Sutton JE (2003) Metacognition in animals: it’s all in the methods. Behav Brain Sci 23:353–354
Smith JD, Beran MJ, Couchman JJ, Coutinho MV (2008) The comparative study of metacognition: sharper paradigms, safer inferences. Psychon Bull Rev 15:679–691
Schwartz BL, Metcalfe J (1994) Methodological problems and pitfalls in the study of human metacognition. In: Metacognition: knowing about knowing 93–113
Kornell N (2009) Metacognition in humans and animals. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 18:11–15
Washburn DA, Smith JD, Shields WE (2006) Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) immediately generalize the uncertain response. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 32:185–189
Metcalfe J (2004) Drawing the line on metacognition. Behav Brain Sci 26:350–351
Glimcher PW (2008) Understanding risk: a guide for the perplexed. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 8:348–354
Gold JI, Shadlen MN (2001) Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli. Trends Cogn Sci 5:10–16
Dayan P, Daw ND (2008) Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 8:429–453
Juslin P, Olsson H (1997) Thurstonian and Brunswikian origins of uncertainty in judgment: a sampling model of confidence in sensory discrimination. Psychol Rev 104:344–366
Vickers D, Pietsch A (2001) Decision making and memory: a critique of Juslin and Olsson’s (1997) sampling model of sensory discrimination. Psychol Rev 108:789–804
Knight F (1921) Risk, ambiguity, and profit. Houghton Mifflin, Boston
Hsu M, Bhatt M, Adolphs R, Tranel D, Camerer CF (2005) Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Am Assoc Adv Sci 310:1680–1683
Glimcher PW (2003) Decisions, uncertainty, and the brain: the science of neuroeconomics. MIT Press, Cambridge
McCoy AN, Platt ML (2005) Risk-sensitive neurons in macaque posterior cingulate cortex. Nat Neurosci 8:1220–1227
Platt ML, Huettel SA (2008) Risky business: the neuroeconomics of decision making under uncertainty. Nat Neurosci 11:398–403
Green DM, Swets JA (1966) Signal detection theory and psychophysics. Wiley, London
Parker AJ, Newsome WT (1998) Sense and the single neuron: probing the physiology of perception. Annu Rev Neurosci 21:227–277
Maniscalco B, Lau H (2012) A signal detection theoretic approach for estimating metacognitive sensitivity from confidence ratings. Conscious Cogn 21:422–430
Kepecs A, Mainen ZF (2012) A computational framework for the study of confidence in humans and animals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1322–1337
Vickers D (1970) Evidence for an accumulator model of psychophysical discrimination. Ergonomics 13:37–58
Moreno-Bote R (2010) Decision confidence and uncertainty in diffusion models with partially correlated neuronal integrators. Neural Comput 22:1786–1811
Zylberberg A, Barttfeld P, Sigman M (2012) The construction of confidence in a perceptual decision. Front Integr Neurosci 6:79
Rolls ET, Grabenhorst F, Deco G (2010) Decision-making, errors, and confidence in the brain. J Neurophysiol 104:2359–2374
Insabato A, Pannunzi M, Rolls ET, Deco G (2010) Confidence-related decision making. J Neurophysiol 104:539–547
Sollich P (2002) Bayesian methods for support vector machines: evidence and predictive class probabilities. Mach Learn 46:21–52
Mazurek ME, Roitman JD, Ditterich J, Shadlen MN (2003) A role for neural integrators in perceptual decision making. Cereb Cortex 13:1257–1269
Bogacz R, Brown E, Moehlis J, Holmes P, Cohen JD (2006) The physics of optimal decision making: a formal analysis of models of performance in two-alternative forced-choice tasks. Psychol Rev 113:700–765
Vickers D, Packer J (1982) Effects of alternating set for speed or accuracy on response time, accuracy and confidence in a unidimensional discrimination task. Acta Psychol (Amst) 50:179–197
Tong S, Koller D (2002) Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. J Mach Learn Res 2:45–66
Rolls ET, Grabenhorst F, Deco G (2010) Choice, difficulty, and confidence in the brain. Neuroimage 53:694–706
Wang XJ (2002) Probabilistic decision making by slow reverberation in cortical circuits. Neuron 36:955–968
Timmermans B, Schilbach L, Pasquali A, Cleeremans A (2012) Higher order thoughts in action: consciousness as an unconscious re-description process. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1412–1423
Juslin P, Olsson H (1999) Computational models of subjective probability calibration. In Juslin P, Montgomery H (eds) Judgment and decision-making: Neo-Brunswickian and process-tracing approaches. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc., Mahwah NJ
Daw ND, O’Doherty JP, Dayan P, Seymour B, Dolan RJ (2006) Cortical substrates for exploratory decisions in humans. Nature 441:876–879
Cohen JD, McClure SM, Yu AJ (2007) Should I stay or should I go? How the human brain manages the trade-off between exploitation and exploration. Philos Trans R Soc B: Biol Sci 362:933
Pessiglione M, Seymour B, Flandin G, Dolan RJ, Frith CD (2006) Dopamine-dependent prediction errors underpin reward-seeking behaviour in humans. Nature 442:1042–1045
Corrado G, Doya K (2007) Understanding neural coding through the model-based analysis of decision making. J Neurosci 27:8178
Sugrue LP, Corrado GS, Newsome WT (2004) Matching behavior and the representation of value in the parietal cortex. Science 304:1782–1787
Barraclough DJ, Conroy ML, Lee D (2004) Prefrontal cortex and decision making in a mixed-strategy game. Nat Neurosci 7:404–410
Lau B, Glimcher PW (2005) Dynamic response-by-response models of matching behavior in rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav 84:555–579
Rolls ET, Grabenhorst F (2008) The orbitofrontal cortex and beyond: from affect to decision-making. Prog Neurobiol 86:216–244
Schoenbaum G, Roesch M (2005) Orbitofrontal cortex, associative learning, and expectancies. Neuron 47:633–636
Elliott R, Friston KJ, Dolan RJ (2000) Dissociable neural responses in human reward systems. J Neurosci 20:6159–6165
Wallis JD (2007) Orbitofrontal cortex and its contribution to decision-making. Annu Rev Neurosci 30:31–56
Mainen ZF, Kepecs A (2009) Neural representation of behavioral outcomes in the orbitofrontal cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19:84–91
Maunsell JH (2004) Neuronal representations of cognitive state: reward or attention? Trends Cogn Sci 8:261–265
Kahneman D, Slovic P, Tversky A (1982) Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York
Kaelbling LP, Littman ML, Cassandra AR (1998) Planning and acting in partially observable stochastic domains. Artif Intell 101:99–134
Volz KG, Schubotz RI, von Cramon DY (2005) Variants of uncertainty in decision-making and their neural correlates. Brain Res Bull 67:403–412
Yu AJ, Dayan P (2005) Uncertainty, neuromodulation, and attention. Neuron 46:681–692
Daw ND, Niv Y, Dayan P (2005) Uncertainty-based competition between prefrontal and dorsolateral striatal systems for behavioral control. Nat Neurosci 8:1704–1711
Fleming SM, Dolan RJ, Frith CD (2012) Metacognition: computation, biology and function. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1280–1286
Stephens DW, Krebs JR (1986) Foraging theory. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Bernstein C, Kacelnik A, Krebs JR (1988) Individual decisions and the distribution of predators in a patchy environment. J Anim Ecol 57:1007–1026
Hayden BY, Pearson JM, Platt ML (2011) Neuronal basis of sequential foraging decisions in a patchy environment. Nat Neurosci 14:933–939
Kamil AC, Misthal RL, Stephens DW (1993) Failure of simple optimal foraging models to predict residence time when patch quality is uncertain. Behav Ecol 4:350–363
Nelson TO, Narens L (1990) Metamemory: a theoretical framework and new findings. Psychol Learn Motiv: Adv Res Theory 26:125–173
Son LK, Metcalfe J (2000) Metacognitive and control strategies in study-time allocation. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 26:204–221
Son LK (2004) Spacing one’s study: evidence for a metacognitive control strategy. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 30:601–604
Son LK, Sethi R (2006) Metacognitive control and optimal learning. Cogn Sci: Multi J 30:759–774
Schohn G, Cohn D (2000) Less is more: active learning with support vector machines. In: Machine learning-international workshop then conference, pp 839–846
Sutton RS (1992) Gain adaptation beats least squares. In: Proceedings of the 7th Yale workshop on adaptive and learning systems, pp 161–166
Dayan P, Kakade S (2001) Explaining away in weight space. Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 451–457
Pearce JM, Hall G (1980) A model for Pavlovian learning: variations in the effectiveness of conditioned but not of unconditioned stimuli. Psychol Rev 87:532–552
Courville AC, Daw ND, Touretzky DS (2006) Bayesian theories of conditioning in a changing world. Trends Cogn Sci 10:294–300
Dearden R, Friedman N, Russell S (1998) Bayesian Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the national conference on artificial intelligence. Wiley, pp 761–768
Strens M (2000) A Bayesian framework for reinforcement learning. In: Machine learning-international workshop then conference, pp 943–950
Knight FH (1921) Risk, uncertainty and profit. Boston and New York
Ernst MO, Bülthoff HH (2004) Merging the senses into a robust percept. Trends Cogn Sci 8:162–169
Körding KP, Wolpert DM (2004) Bayesian integration in sensorimotor learning. Nature 427:244–247
Graf EW, Warren PA, Maloney LT (2005) Explicit estimation of visual uncertainty in human motion processing. Vision Res 45:3050–3059
Körding KP, Wolpert DM (2006) Bayesian decision theory in sensorimotor control. Trends Cogn Sci 10:319–326
Deneve S (2008) Bayesian spiking neurons I: inference. Neural Comput 20:91–117
Bang D, Mahmoodi A, Olsen K, Roepstorff A, Rees G, Frith C, Bahrami B (2014) What failure in collective decision-making tells us about metacognition. In: Fleming SM, Frith C (eds) The cognitive neuroscience of metacognition. Springer, Berlin
Montague PR, Berns GS (2002) Neural economics and the biological substrates of valuation. Neuron 36:265–284
Sugrue LP, Corrado GS, Newsome WT (2005) Choosing the greater of two goods: neural currencies for valuation and decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:363–375
Padoa-Schioppa C, Assad JA (2006) Neurons in the orbitofrontal cortex encode economic value. Nature 441:223–226
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to our collaborators and members of our groups for discussions. Preparation of this article was supported by the Klingenstein, Sloan, Swartz, and Whitehall Foundations to A.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kepecs, A., Mainen, Z.F. (2014). A Computational Framework for the Study of Confidence Across Species. In: Fleming, S., Frith, C. (eds) The Cognitive Neuroscience of Metacognition. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45190-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45190-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-45189-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-45190-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)