Abstract
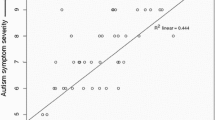
A striking deficiency in the physiologic modulation of sensory stimuli can be inferred from clinical observation of autistic behavior (Ornitz, 1969, 1970, 1973, 1974; Goldfarb, 1961, 1963; Bergman & Escalona, 1949). All sensory modalities are affected and the faulty modulation of sensory input may be manifest as either a lack of responsiveness or an exaggerated reaction to sensory stimuli (Goldfarb, 1961, 1963). This faulty modulation of sensory input is an intrinsic feature of the autistic behavioral syndrome. This is demonstrated by the responses of parents of 74 young (mean age 45.2 months) autistic children to a standard set of questions about their child’s development. Tables 1 through 3 list some of the most predominant symptoms reported by the parents in the behavioral categories of autistic disturbances of relating, perception, and motility* and indicate the percent of this population of autistic children who were reported to exhibit each behavior. It can be seen from these tables that symptoms in the category of autistic disturbances of the modulation of sensory input occur at high frequencies as do symptoms in the category of autistic disturbances of relating. Furthermore, the occurrences of many of these symptoms are highly correlated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aschan, G., & Bergstedt, M. The genesis of secondary nystagmus induced by vestibular stimuli. Acta Societatis Medicorum Upsaliensis, 1955,60, 113–122.
Bender, L. Childhood schizophrenia. Clinical study of one hundred schizophrenic children. American Journal of Orothpsychiatry, 1947, 17, 40–56.
Bender, L. Schizophrenia in childhood—Its recognition, description, and treatment.American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 1956, 26, 499–506.
Bender, L. A longitudinal study of schizophrenic children with autism. Hospital and Community Psychiatry, 1969, 20, 230–237.
Bender, L. The life course of children with autism and mental retardation. In F. J. Menolascino (Ed.), Psychiatric approaches to mental retardation. New York: Basic Books, Inc., 1970. Pp. 149–191.
Bender, L., & Faretra, G. The relationship between childhood schizophrenia and adult schizophrenia. In A. R. Kaplan (Ed.), Genetic factors in “schizophrenia.” Springfield, Ill: Charles C Thomas, 1972.
Bender, L., & Freedman, A. M. A study of the first 3 years in the maturation of schizophrenic children. Quarterly Journal of Child Behavior, 1952, 4, 245–272.
Bender, L., & Helme, W. H. A quantitative test of theory and diagnostic indicators of childhood schizophrenia. A.M.A. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry, 1953, 70, 413–427.
Bergman, P., & Escalona, S. K. Unusual sensitivities in very young children. Psychoanalytic Study of the Child, 1949, 3–4, 333–353.
Bernal, M. E., & Miller, W. H. Electrodermal and cardiac responses of schizophrenic children to sensory stimuli. Psychophysiology, 1970, 7, 155–168.
Colbert, E., & Koegler, R. Toe walking in childhood schizophrenia. Journal of Pediatrics, 1958, 53, 219–220.
Colbert, E. G., Koegler, R. R., & Markham, C. H. Vestibular dysfunction in childhood schizophrenia. A.M.A. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1959, 7, 600–617.
Collins, W. E. Vestibular responses from figure skaters. Aerospace Medicine, 1966, 37, 1098–1104.
Collins, W. E. Special effects of brief periods of visual fixation on nystagmus and sensations of turning. Aerospace Medicine, 1968, 59, 257–266.
Creak, M., & Pampiglione, G. Clinical and EEG studies on a group of 35 psychotic children. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 1969, 11, 218–227.
Dichgans, J., & Brandt, T. Optokinetic motion sickness and pseudo-coriolis effects induced by moving visual stimuli. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1973, 76, 339–348.
Dix, M. R., & Hood, J. D. Observations upon the nervous mechanism of vestibular habituation.Oto-Laryngologica, 1969, 67, 310–318.
Fish, B. The study of motor development in infancy and its relationship to psychological functioning. American Journal of Psychiatry, 1961, 117, 1113–1118.
Frith, U., & Hermelin, B. The role of visual and motor cues for normal, subnormal and autistic children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 1969, 10, 153–165.
Goldberg, J. M., & Fernandez, C. Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. I. Resting discharge and response to constant angular accelerations. Journal of Neurophysiology, 1971, 34, 635–684.
Goldfarb, W. Childhood schizophrenia. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1961.
Goldfarb, W. Self-awareness in schizophrenic children. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1963, 8, 47–60.
Goodwin, M. S., Cowen, M. A., & Goodwin, T. C. Malabsorption and cerebral dysfunction: A multivariate and comparative study of autistic children.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1911, 1, 48–62.
Hermelin, B., & O’Connor, N. Measures of the occipital alpha rhythm in normal, subnormal and autistic children. British Journal of Psychiatry, 1968, 114, 603–610.
Hermelin, B., & O’Connor, N. Psychological experiments with autistic children. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1970.
Honrubia, V., Streliofif, D., & Ward, P. H. Computer analysis of nystagmus induced by constant angular accelerations in normal and labyrinthectomized cats. Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 1973, 79, 254–265.
Hood, J. D. The clinical significance of vestibular habituation. Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 1970, 17, 149–157.
Hutt, C., Forrest, S. J., & Richer, J. Cardiac arrhythmia and behavior in autistic children. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 1975, 19, 361–372.
Hutt, C., Hutt, S. J., Lee, D., & Ounsted, C. A behavioural and electroencephalographic study of autistic children. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 1965, 3, 181–197.
Kolvin, I., Ounsted, C., & Roth, M. Six studies in the childhood psychoses. V. Cerebral dysfunction and childhood psychoses. British Journal of Psychiatry, 1971, 118, 407–414.
Lachenbruch, P. A. Discriminant analysis. New York: Hafner Press, 1975.
Laffont, F., Sauvage, D., & Lelord, G. Activité lente corticale succédant au mouvement volontaire chex l’homme. Comptes Rendus des Séances de la Société de Biologie et de Ses Filiales (Paris), 1971, 165, 660–665.
Lelord, G., Laffont, F., Jusseaume, P., & Stephant, J. L. Comparative study of conditioning of averaged evoked responses by coupling sound and light in normal and autistic childrtn. Psychophysiology, 1973, 70, 415–425.
MacCulloch, M. J., Williams, C., & Davies, P. Heart-rate variability in a group of cerebral palsied children. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 1971, 13, 645–650.
Malcolm, R., & Jones, G. M. A quantitative study of vestibular adaptation in humans. Oto-Laryngologica, 1970, 70, 126–135.
Marshall, J. E., & Brown, J. H. Visual-arousal interaction and specificity of nystagmic h2Lbitu2iiion.Aerospace Medicine, 1967, 38, 597–599.
Miller, W. H., & Bernai, M. E. Measurement of the cardiac response in schizophrenic and normal children. Psychophysiology, 1971, 8, 533–537.
Onheiber, P., White, P. T., DeMyer, M. K., & Ottinger, D. R. Sleep and dream patterns of child schizophrenics. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1965, 12, 568–571.
Ornitz, E. M. The disorders of perception common to early infantile autism and schizophrenia. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 1969, 10, 259–274.
Ornitz, E. M. Vestibular dysfunction in schizophrenia and childhood autism. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 1970, 77, 159–173.
Ornitz, E. M. Development of sleep patterns in autistic children. In C. D. Clemente, D. Purpura, & F. Mayer (Eds.), Sleep and the maturing nervous system. New York: Academic Press, 1972.
Ornitz, E. M. Childhood autism: A review of the clinical and experimental literature. California Medicine, 1973, 118, 21–47.
Ornitz, E. M. The modulation of sensory input and motor output in autistic children. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1974, 4, 197–215.
Ornitz, E. M., Brown, M. B., Mason, A., & Putnam, N. H. The effect of visual input on postrotatory nystagmus in normal children. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1974, 77, 418–425. (a)
Ornitz, E. M., Brown, M. B., Mason, A., & Putnam, N. H. The effect of visual input on vestibular nystagmus in autistic children. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1974, 31, 369–375. (b)
Ornitz, E. M., Brown, M. B., Sorosky, A. D., Ritvo, E. R., & Dietrich, L. Environmental modification of autistic behavior. of General Psychiatry, 1970, 22, 560–565.
Ornitz, E. M., Forsythe, A. B., & de la Peña, A. The effect of vestibular and auditory stimulation on the REMs of REM sleep in autistic children. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1973, 29, 786–791. (a)
Ornitz, E. M., Forsythe, A. B., Tanguay, P. E., Ritvo, E. R., de la Peña, A., & Ghahremani, J. The recovery cycle of the averaged auditory evoked response during sleep in autistic children. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1974, 37, 173–174. (c)
Ornitz, E. M., Guthrie, D., & Farley, A. J. The early symptoms of childhood autism. Presented at Kittay Scientific Foundation Symposium, “Cognitive Defects in the Development of Mental Illness,” in press.
Ornitz, E. M., & Ritvo, E. R. Perceptual inconstancy in early infantileautism. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1968, 18, 76–98.
Ornitz, E. M., Ritvo, E. R., Brown, M. B., LaFranchi, S., Parmelee, T., & Walter, R. D. The EEG and rapid eye movements during REM sleep in normal and autistic children. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1969, 26, 167–175. (a)
Ornitz, E. M., Ritvo, E. R., Lee, Y. H., Panman, L. M., Walter, R. D., & Mason, A. The auditory evoked response in babies during REM sleep. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1969, 27, 195–198. (b)
Ornitz, E. M., Ritvo, E. R., Panman, L. E., Lee, Y. H., Carr, E. M., & Walter, R. D. The auditory evoked response in normal and autistic children during sleep. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1968, 25, 221–230.
Ornitz, E. M., Ritvo, E. R., & Walter, R. D. Dreaming sleep in autistic and schizophrenic children. American Journal of Psychiatry, 1965, 122, 419. (a)
Ornitz, E. M., Ritvo, E. R., & Walter, R. Dreaming sleep in autistic twins. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1965, 12, 77–79. (b)
Ornitz, E. M., Tanguay, P. E., & Lee, J. C. M. The recovery function of the auditory evoked response during sleep in children. In U. J. Jovanovic (Ed.), The nature of sleep. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer Verlag, 1973. (b)
Ornitz, E. M., Tanguay, P. E., Lee, J. C. M., Ritvo, E. R., Sivertsen, B., & Wilson, C. The effect of stimulus interval on the auditory evoked response during sleep in autistic children. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1972, 2, 140–150.
Ornitz, E. M., Wechter, V., Hartman, D., Tanguay, P. E., Lee, J. C. M., Ritvo, E. R., & Walter, R. D. The EEG and rapid eye movements during REM sleep in babies. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1911, 30, 350–353.
Pfaltz, C. R., & Ohtsuka, Y. The influence of optokinetic training upon vestibular habituation.Oto-Laryngologica, 1975, 79, 253–258.
Pfaltz, C. R., & Piffko, P. Studies on habituation of the human vestibular sysXtm. Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 1970, 17, 169–179.
Pollack, M., & Krieger, H. P. Oculomotor and postural patterns in schizophrenic children. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry, 1958, 79, 720–726.
Pompeiano, O. The neurophysiological mechanisms of the postural and motor events during desynchronized sleep. Research Publications of the Association for Research in Nervous and Mental Disease, 1967, 45, 351–423.
Pompeiano, O., & Morrison, A. R. Vestibular influences during sleep. I. Abolition of the rapid eye movements during desynchronized sleep after vestibular lesions. Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 1965, 103, 569–595.
Rapin, I. Hypoactive labyrinths and motor development. Clinical Pediatrics, 1974, 13, 922–937.
Ritvo, E. R., Ornitz, E. M., Eviatar, A., Markham, C. H., Brown, M. B., & Mason, A. Decreased postrotatory nystagmus in early infantile autism. Neurology, 1969, 19, 653–658.
Ritvo, E. R., Ornitz, E. M., & LaFranchi, S. Frequency of repetitive behaviors in early infantile autism and its variants. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1968, 19, 341–341.
Rutter, M. Psychotic disorders in early childhood. In A. J. Coppen & A. Walk (Eds.), Recent developments in schizophrenia—A symposium. London: RMPA; Ashford, Kent: Headley Bros., 1967. Pp. 133–158.
Small, J. G. Sensory evoked responses of autistic children. In D. W. Churchill, G. D. Alpern, & M. DeMyer (Eds.), Infantile autism: Proceedings of the Indiana University Colloquium. Springfield, Ill.: Charles C Thomas, 1971. Pp. 224–242.
Small, J. G. EEG and neurophysiological studies of early infantile autism. Biological Psychiatry, 1975, 10, 385–398.
Small, J. G., DeMyer, M. K., & Milstein, V. CNV responses of autistic and normal children. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1971, 1, 215–231.
Sorosky, A. D., Ornitz, E. M., Brown, M. B., & Ritvo, E. R. Systematic observations of autistic behavior. Archives of General Psychiatry, 1968, 18, 439–449.
Stockwell, C. W., Gilson, R. D., & Guedry, F. E., Jr. Adaptation of horizontal semicircular canal responses. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1973, 75, 471–476.
Tjernström, Ö. Nystagmus inhibition as an effect of eye closure. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1973, 75, 408–418.
Walter, D. O., Berkhout, J. I., Buchness, R., Kram, E., Rovner, L., & Adey, W. R. Digital computer analysis of neurophysiological data from Biosatellite 111.Aerospace Medicine, 1911, 42, 314–321.
Wasman, M., Morehead, S. D., Lee, H. Y., & Rowland, V. Interaction of electroocular potentials with the contingent negative variation. Psychophysiology, 1970, 7, 103–111.
Wendt, G. R. Vestibular functions. In S. S. Stevens (Ed.), Handbook of experimental psychology. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1951. Pp. 1191–1223.
Young, L. R., Dichgans, J., Murphy, R., & Brandt, T. Interaction of optokinetic and vestibular stimuli in motion perception. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1973, 76, 24–31.
Young, L. R., & Henn, V. S. Selective habituation of vestibular nystagmus by visual stimulation.Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 1974, 77, 159–166.
Young, L. R., & Oman, C. M. Model for vestibular adaptation to horizontal rotation. Aerospace Medicine, 1969, 40, 1076–1079.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1978 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ornitz, E.M. (1978). Neurophysiologic Studies. In: Rutter, M., Schopler, E. (eds) Autism. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0787-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0787-7_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-0789-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-0787-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive