Abstract
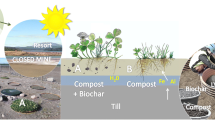
A series of single extractions and short-term plant tests were performed in order to test a variety of inexpensive mineral amendments for the in situ inactivation of trace elements on the fine-grained spoil of the former gold mine of Jales, Portugal. Based on the results of these tests, mesocosms (lysimeters) were constructed and a small-scale semi-field trial was carried out since 1998. The long-term effect of steelshots (SS, iron grit), beringite (B), and municipal compost (C) as spoil amendments was investigated. Vegetation establishment on the treated spoils was successful with Holcus lanatus L. in year 1 and Pinus pinaster Ait. in year 2. Therefore, a detailed monitoring program was implemented for determining the sustainability of trace elements in situ inactivation by C (5%), CB (5% compost combined with 5% beringite), CSS (5% compost combined with 1% steelshots), and CBSS (5% compost combined with 5% beringite and 1% steelshots) treatments (all amendments are expressed by soil dry weight) and of the revegetation. After 3 years, revegetation was excellent in the CSS treatment, and successful for the CBSS. Volunteer plant species became established in treated spoils during year 2. In contrast, the trees planted on the C treated spoil declined from year 2 and some died. In year 3, the trees on the CB treatment started to decline. Arsenic and zinc exposure are suggested to explain the negative effects on pine growth. In agreement with results of single extractions, compost addition in the spoil increased long-term arsenic percolation. Lead leaching was also enhanced. The CBSS and CSS treatments were the most effective for limiting water-soluble As and decreasing long-term metal leaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway B J 1995 Heavy Metals in Soils. 2nd edition. Blackie Academic Professional, Glasgow, UK. 368 pp.
Balabane M, Faivre D, van Oort F and Dahmani-Muller H 1999 Mutual effects of soil organic matter dynamics and heavy metal fate in a metallophyte grassland. Environ. Poll. 105, 45–54.
Bleeker P M, De Koe T and Assunção A L 1999 Remediation of the Jales minespoil by inactivation and phytostabilisation: on site experiments. In Proc. Extended Abstracts 5th Int. Conf. Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Vienna’ 99. Eds. W W Wenzel, D C Adriano, B Alloway, H E Doner, C Keller, N W Lepp, M Mench, R Naidu and GM Pierzynski. pp. 866–867. Int Soc Trace Element Research, Vienna.
Bleeker P M, Assunção A G L, Teiga P M, De Koe T and Verkleij J A C 2002 Revegetation of the acidic, As contaminated Jales mine spoil tips using a combination of spoil amendments and tolerant grasses. Sci. Tot. Environ. (in press).
Boisson J 1999 Réhabilitation de sols pollués en éléments traces par des amendements minéraux. PhD thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Nancy. 188 pp.
Boisson J, Mench M, Sappin-Didier V, Solda P and Vangronsveld J 1998. Short-term in situ immobilization of Cd and Ni by beringite and steel shots application to long-term sludged plots. Agronomie 18, 347–359.
Boisson J, Morel C and Mench M 1999 Arsenate exchange between soil and solution in soils treated with steelshots and beringite. In Proc. Extended Abstracts 5th Int. Conf. Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Vienna’ 99. Eds.W W Wenzel, D C Adriano, B Alloway, H E Doner, C Keller, N W Lepp, M Mench, R Naidu and G M Pierzynski. pp. 1010–1011. Int Soc Trace Element Research, Vienna, Austria.
Briers S 1998 Studie van de invloed van arseen op een aantal facetten van het plantmetabolisme bij Phaseolus vulgaris en Zea mays. Ongepubliceerde licentiatsthesis, Universiteit Antwerpen, UIA, Antwerpen.
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment 2001 Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, CCME Documents, Winnipeg.
De Koe T 1994 Arsenic resistance in submediterranean Agrostis species. PhD thesis, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, NL. 127 p.
De Koe T, Canteiro S F, Assunção A L and Bleeker P M 1998 Field experiments, Contractor 5 In Strategies for Rehabilitation of Metal Polluted Soils: in situ Phytoremediation, Immobilization and Revegetation, a Comparative Study (PHYTOREHAB). Eds. J A C Verkleij, S Karenlampi, T De Koe, M Mench and J Vangronsveld. Progress report no. 5 ENV4-CT95–0083, EU DGXII Environment & Climate Programme. pp. 44–67. Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam.
Delschen T 1999. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated gardens by soil covering. In Proc. Extended Abstracts 5th Int. Conf. Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Vienna’ 99. Eds. W W Wenzel, D C Adriano, B Alloway, H E Doner, C Keller, N W Lepp, M Mench, R Naidu and G M Pierzynski. pp. 986–987. Int Soc Trace Element Research, Vienna.
Ferguson C C 1999 Assessing risks from contaminated sites: Policy and practice in 16 European countries. Land Contam. Reclam. 7, 33–54.
Knox A S, Seaman J, Mench M and Vangronsveld J 2001 Remediation of metal-and radionuclide-contaminated soils by in-situ stabilisation techniques. In Environmental Restoration of Metals Contaminated Soils. Ed. I K Iskandar. pp. 21–60. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Lebourg A, Sterckeman T, Cieselski H, Proix N and Gomez A1996 Estimation of soil trace metal bioavailability using unbuffered salt solutions: degree of saturation of polluted soil extracts. Environ. Technol. 19, 243–252.
Lagriffoul A 1998 Biomarqueurs métaboliques de toxicité du cadmium chez lemaïs (Zea mays L.).Mécanismes de tolérance, relations dose-effet et précocité de la réponse. PhD thesis, Université Bordeaux I, Bordeaux. 324 pp.
Macnicol R D and Beckett P H T 1985 Critical tissue concentrations of potentially toxic elements. Plant Soil 85, 107–129.
McBride M B and Martinez C E 2000 Copper phytotoxicity in a contaminated soil: remediation tests with adsorptive materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 4386–4391.
Mench M, De Koe T, Vangronsveld J, Bussière S, Boisson J and Masson P 1999 Remediation of the Jales mine spoil by inactivation and phytostabilisation: study in lysimeters. In Proc. Extended Abstracts 5th Int. Conf. Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements, Vienna’ 99. Eds.W W Wenzel, D C Adriano, B Alloway, H E Doner, C Keller, N W Lepp, M Mench, R Naidu and G M Pierzynski. pp. 914–915. Int. Soc Trace Element Research, Vienna, Austria.
Mench M, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H, Lepp N W and Edwards R 2000 In situ metal immobilisation and phytostabilisation of contaminated soils. In Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soil and Water. Eds. N Terry and G Bañuelos. pp. 323–358. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL.
Mench M, Vangronsveld J, Lepp N W, Bleeker P and Ruttens A 2002. Use of amendments to attenuate trace element exposure: sustainability, side effects and failures. In Natural Attenuation of Trace Element Availability in Soils, Eds. R Hamon and M McLaughlin, SETAC (submitted).
Peters T H 1995 Revegetation of the Copper Cliff tailings area. In Restoration and Recovery of an Industrial Region. Progress in Restoring the Smelter-Damaged Landscape near Sudbury, Canada. Ed. J M Gunn. pp. 123–134. Springer, New York.
Santos Oliveira J M and Freira Avila E P 1995 Avaliação do impacto quimico ambiental provocado por uma exploração mineira. Um caso de estudo na Mina de Jales. Estud. Nota Trabalhos 37, 25–50.
Tisch B, Beckett P, Okonski A, Gordon C and Spiers G 2000 Remediation and revegetation of barren copper tailings using paper mill sludge; an overview. CLRA Annual Meeting, Sept. 2000, Edmonton, Alberta.
Vangronsveld J and Clijsters H 1992 A biological test system for the evaluation of metal phytotoxicity and immobilization by additives in metal contaminated soils. In Metal Compounds in Environment and Life, 4 (Interrelation Between Chemistry and Biology). Eds. E Merian and W Haerdi. pp. 117–125. Science and Technology Letters, Northwood, UK.
Vangronsveld J and Cunningham S 1998 In situ Inactivation and Phytorestoration of Metal-Contaminated Soils. Landes Biosciences, Georgetown, TX. 265 pp.
Vangronsveld J, Ruttens A, Clijsters H 1999 The use of cyclonic ashes of fluidized bed burning of coal mine refuse for long-term immobilization of metals in soils. In Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements in Coal and Coal Combustion By-Products. Eds K S Sajwan, A K Alva and R F Keefer. pp. 223–233. Plenum/Kluwer Academic Publishing, New York.
Verkleij J A C, Karenlampi S, De Koe T, Mench M and Vangronsveld J 1999. Strategies for rehabilitation of metal polluted soils: in situ phytoremediation, immobilization and revegetation, a comparative study (PHYTOREHAB). Final report ENV4-CT95–0083, EU DGXII Environment & Climate programme, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam.
Walsh L M and Keeney D R 1975. Behaviour and phytotoxicity of inorganic arsenicals in soils. In Arsenical Pesticides. Ed E A Woolson. American Chemical Society Symposium, Vol. 7. pp. 35–52. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mench, M., Bussière, S., Boisson, J. et al. Progress in remediation and revegetation of the barren Jales gold mine spoil after in situ treatments. Plant and Soil 249, 187–202 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022566431272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022566431272